Evacuees in Philippines, Taiwan take shelter as Super Typhoon Nando nears
Hundreds of families sheltered in schools and evacuation centers on Monday as heavy rains and gale-force winds from Super Typhoon Nando (international name: Ragasa) lashed northern Philippines and southern Taiwan.
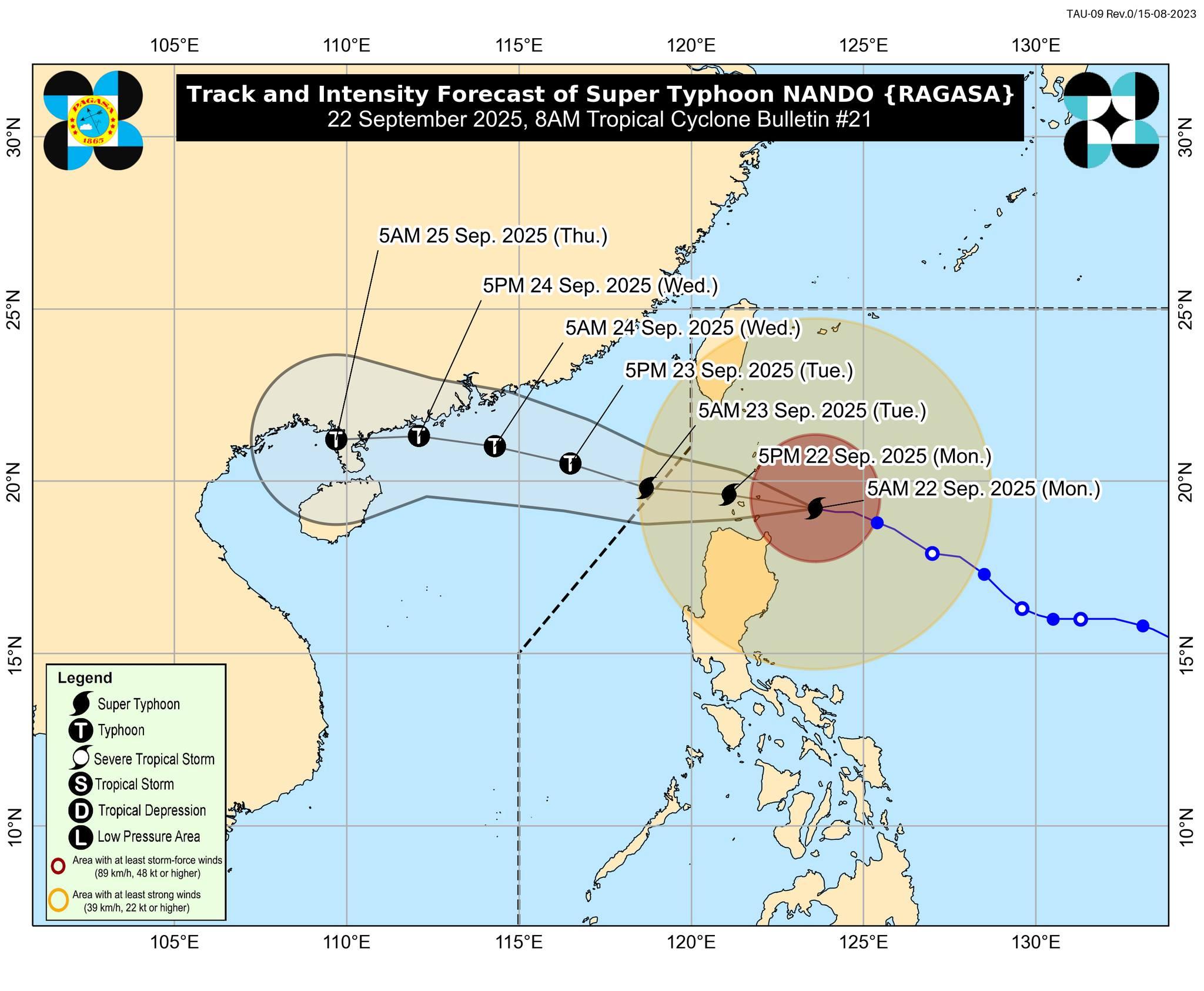
The typhoon, which is gaining strength as it proceeds on a collision course with southern China, was expected to make landfall over the Philippines' Babuyan Islands by around midday.
The sparsely populated islands lie about 740 kilometers (460 miles) south of Taiwan in the Luzon Strait.
As of 8:00 am (0000 GMT), maximum sustained winds of 215 kilometers per hour were reported at the storm's center, with gusts reaching up to 265 kph as it moved toward the archipelago nation, the national weather service said.
"We are now experiencing strong winds here in northern Cagayan," provincial disaster chief Rueli Rapsing told AFP, saying they were prepared for "the worst."
"Since the super typhoon will traverse Calayan, we are very focused on that area," he said of a town in the far north province.
Taiwan situation
In Taiwan, small-scale evacuations were ongoing in mountainous areas near Pingtung, local fire department officer James Wu told AFP.
"What worries us more is that the damage could be similar to what happened during Typhoon Koinu two years ago," he added, describing a storm that saw utility poles collapse and sheet-metal roofs sent flying into the air.
Schools and government offices were closed Monday in Metro Manila and across 29 Philippine provinces in anticipation of heavy rainfall.
Government weather specialist John Grender Almario said Sunday that "severe flooding and landslides" could be expected in the northern areas of the main island Luzon.
The Philippines is the first major landmass facing the Pacific cyclone belt, and the archipelago is hit by an average of 20 storms and typhoons each year, putting millions of people in disaster-prone areas in a state of constant poverty.
Scientists warn that storms are becoming more powerful as the world warms due to the effects of human-driven climate change. — Agence France-Presse




